Serendip is an independent site partnering with faculty at multiple colleges and universities around the world. Happy exploring!

- home
- education
- science
- Minds-on Activities for Teaching Biology
- Next Generation Science Standards
- Remote Ready Biology Activities
- NGSS Biology Activities
- Hands-On Activities for Teaching Biology
- Teaching Climate Change
- Science Education
- Summer Institutes for K-12 Teachers 1995-2010
- Brain & Behavior
- Biology
- Science & Culture
- Complex Systems
- digital humanities
- play
- one world
 © Serendip® 1994 - All rights reserved. Privacy Policy
© Serendip® 1994 - All rights reserved. Privacy Policy
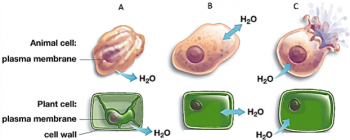 In this hands-on, minds-on activity, students investigate the effects of hypotonic and hypertonic solutions on eggs that have had their shells removed. As students interpret their results, they develop a basic understanding of the process of osmosis. As they answer additional analysis and discussion questions, students learn about the effects of osmosis on animal and plant cells and apply their understanding of osmosis to the interpretation of several “real-world” phenomena.
In this hands-on, minds-on activity, students investigate the effects of hypotonic and hypertonic solutions on eggs that have had their shells removed. As students interpret their results, they develop a basic understanding of the process of osmosis. As they answer additional analysis and discussion questions, students learn about the effects of osmosis on animal and plant cells and apply their understanding of osmosis to the interpretation of several “real-world” phenomena.