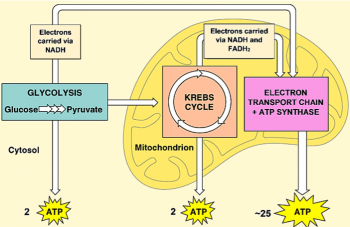
In both versions of the Student Handout, students analyze two models of cellular respiration. The first model shows chemical equations that summarize the inputs and outputs of cellular respiration. The second model is a figure that shows the three major stages of cellular respiration and the role of mitochondria.
After students analyze these models, they use what they have learned to develop their own more complete model of cellular respiration.
Then, in the advanced version of the Student Handout, students analyze how the extensive, folded inner membrane of a mitochondrion contributes to ATP production. This analysis illustrates the general principle that structure is related to function.
The simpler version of the Student Handout is available in the first two attached files and in a Google Doc. The advanced version of the Student Handout is available in the third and fourth attached files and in a Google Doc. The Teacher Notes, available in the last two attached files, provide background information and instructional suggestions and explain how this activity is aligned with the Next Generation Science Standards.

 © Serendip® 1994 - All rights reserved. Privacy Policy
© Serendip® 1994 - All rights reserved. Privacy Policy
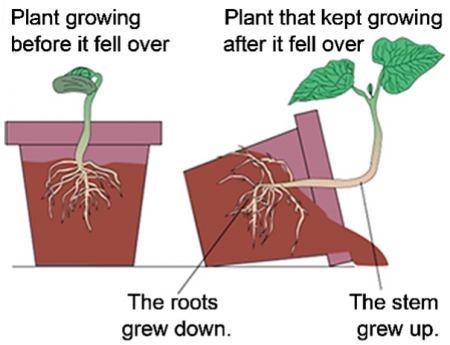 In this analysis and discussion activity, students investigate several examples of plants that have grown in odd shapes.
In this analysis and discussion activity, students investigate several examples of plants that have grown in odd shapes.