In this analysis and discussion activity, students develop their understanding of the exponential and logistic population growth models by analyzing the recovery of endangered species and growth of bacterial populations. Students learn about the processes that cause exponential or logistic population growth, interpret data from several investigations, and apply their understanding to policy questions.
Next, students analyze examples where the trends in population size do not match the predictions of the exponential or logistic population growth models. They learn that models are based on simplifying assumptions and a model’s predictions are only accurate when the simplifying assumptions are true for the population studied.
In the last section, students analyze trends in human population size and some of the factors that affect the earth’s carrying capacity for humans.
One version of the Student Handout also includes mathematical equations for exponential and logistic population growth. Appendices to these Teacher Notes offer optional questions on food poisoning, exponential growth of a rabbit population, additional examples of exceptions to the logistic population growth model, and a research challenge (to develop proposals for sustainable use of two resources that may limit the earth’s carrying capacity for humans).

 © Serendip® 1994 - All rights reserved. Privacy Policy
© Serendip® 1994 - All rights reserved. Privacy Policy

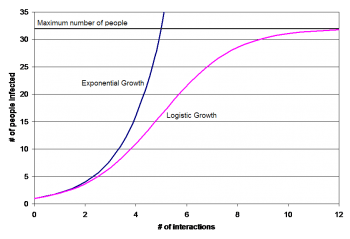 First, students analyze a hypothetical example of exponential growth in the number of infected individuals.
First, students analyze a hypothetical example of exponential growth in the number of infected individuals.