Serendip is an independent site partnering with faculty at multiple colleges and universities around the world. Happy exploring!
biology

Gender and Sexuality in the High School Biology Classroom: Fostering Critical Thinking and Active Engagement
Gender and Sexuality in the High School Biology Classroom:
Fostering Critical Thinking and Active Engagement
Summary: This project was undertaken with the hope of changing the ways we think about teaching and engaging with science. This paper will discuss ways to help students recognize that science is interdisciplinary and can both affect and be affected by the social and/or political context it exists in.
By asking students to think about the way science is presented and conducted, and giving them the tools to think about science not as an isolated body of information, but as a dynamic and shifting discipline, we will not only be encouraging more engaged science scholarship, but will also help students begin to notice the ways science is used as evidence in different contexts and evaluate these uses.
Objective:
The goals of this project are two-fold. I hope to suggest ways for biology teachers:
A response to “Miss Representation 8 min. trailer:” Changing gender stereotypes by increasing visibility of female athletes
The trailer for Miss Representation by filmmaker Jennifer Siebel Newsom describes the power of the media, acknowledging that people learn more from it than any other single source of information. The media is the primary force that shapes our society: “politics, national discourse, and children’s brains, lives, and emotions” (Jim Steyer, CEO, Common Sense Media). Upwards of one billion people use the Internet every day (Marissa Mayer, Vice President, Consumer Products, Google); images are widely available and accessible without restrictions.
The messages disseminated by the mainstream media are pervasive, and more often than not emphasize and perpetuate harmful gender stereotypes. According to Miss Representation, women hold only 3% of clout positions in telecommunications, entertainment, publishing and advertising and comprise just 16% of all writers, directors, producers, cinematographers and editors. Because women are generally not the ones deciding how they are represented in the media, they are often shown as sex objects, valued by their looks rather than their achievements. As a result, “girls are taught that their value is based on how they look, and boys are taught that that’s what’s important about women” (Jean Kilbourne, EdD, Filmmaker, Killing Us Softly).


Dear Middleschoolers, Love, Charlie
Dear boys, girls, and those of you who just aren’t quite sure yet (because that is totally cool too),
For many of you, this is a confusing time. Things are growing in places where you aren’t sure if they are supposed to be growing, new places might develop novel smells, and you might start to feel differently. If any of these things apply to you, or if none of these things apply to you, you are still normal. Every body goes through different changes at different speeds and in completely different orders. So if your best friend is growing armpit hair, but you haven’t reached that point yet, don’t worry – we all catch up in the end! I am writing to you, middle-schoolers, because this time can be a bit scary; there are a lot of changes that you can expect in the next couple of years, and a lot of information out there, both true and false, so a quick guide to the next few years seems like a pretty good resource for you right about now. Read on to learn about what makes boys and girls different biologically, some of the changes that you can expect to your body during puberty, how babies are made, and a quick peek at the different categorizations of gender!
Let’s start from the very beginning. How did we get here and what exactly makes girls different from boys?
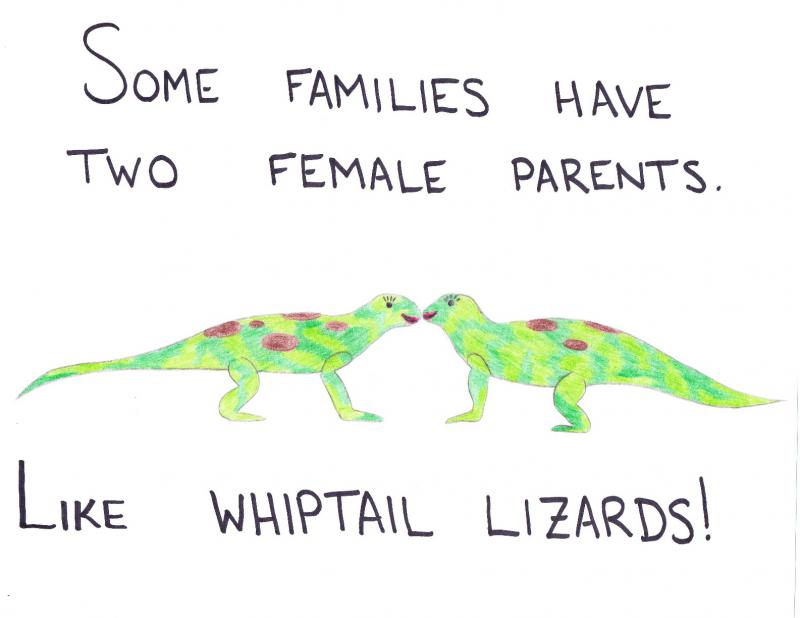













 This activity is aligned with the Next Generation Science Standards. The attached files have the overview of key concepts, with descriptions of relevant learning activities and links to the activities.
This activity is aligned with the Next Generation Science Standards. The attached files have the overview of key concepts, with descriptions of relevant learning activities and links to the activities.