
|

|
|
|
What happens when we age?
Have you ever considered what happens to our brains as we get older? For example, most brains shrink considerable in size after age 20. A brain of an 80 year old weighs approximately 10% less than the brain of a 20 year old of the same body size and sex. Do changes in brain size cause changes in behavior? We've seen in previous animal examples that changes in the structure or function of a brain are accompanied by changes in behavior. So, what about in this case of human aging?
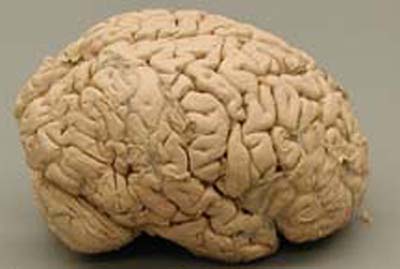   Does a smaller brain mean decreased intelligence or abilities? Well, first of all, we can definitely say that a smaller brain does not equate with a smaller IQ. Indeed, there is considerable variation in human brain size . . . and this is not necessarily reflective of intelligence. (Click here for a more detailed discussion of brain size and intelligence) This changing of the brain is considered normal in the aging process. Different regions of the brain are affected by cell loss and shrinkage, such as the cerebral cortex. Some receptors on cells become more sensitive to particular chemicals. Some expression of neurotransmitters (such as acetylcholine, GABA, norepinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine) begins to decrease. This is within the typical scope of aging . . . and of course older people behave differently than younger people.
 In the case of aging, could extreme changes in the brain be accompanied by extreme changes in behavior? In the case of aging, could extreme changes in the brain be accompanied by extreme changes in behavior?
HOME || VARIATION || PATHOLOGY || GENDER & SEXUAL ORIENTATION || BIBLIOGRAPHY
|